LTE Architecture
LTE network compromises of the following nodes:
LTE network compromises of the following nodes:
- UE (User Endpoint)
- MME (Mobile Management Entity)
- S-GW (Serving Gateway)
- P-GW (PDN Gateway)
- PDN (Packet Data Network or IP world)
- PCRF (Policy and Charging Enforcement Function)
- eNB (e Node B)
- SGSN (Serving GPRS Support Node)
- HSS (Home Subscriber SubSystem)
- E-UTRAN (Collection of eNB)
- EPC (Combination of MME, S-GWand P-GW)
The Architecture of LTE network look like this:
 |
| LTE Non-Roaming architecture |
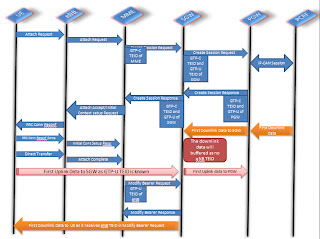
The communication between different nodes of LTE work like this:
We will go deeper to describe about the different interface between different nodes, functionality and the layering structure of LTE Nodes.
Interfaces between different Nodes:
Uu-Interface: This interface is in between UE and eNB. This is a radio/air interface and OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple access) technology is used to send uplink packet and SC-FDMA technology is being used to send downlink packet.
X2-Interface: This interface is in between eNB and eNB. Under this interface the UDP being used as Transport protocol and GTP being used as Application protocol. Basically this interface is used for Handover.
S1-U Interface: This interface is in between eNB and S-GW and this interface will be used for data path communication. Under this interface UDP will be used as Transport protocol and GTP-U protocol will be used for application protocol
S1-AP Interface: This interface is in between eNB and MME. This interface is used for sending signalling packet between eNB and MME. Under this interface SCTP will be used as transport protocol and S1-AP will be used as application protocol.
S11 Interface: This interface is in between MME and S-GW. this interface will be used for Signalling communication between MME and S-GW. Under this interface UDP will be used as transport protocol and GTP-C will be used as application protocol.
S5-C Interface: This interface is in between S-GW and P-GW. This interface will be used for signalling between S-GW and P-GW. Under this interface UDP will be used for transport protocol and GTP-C will be used for applicatio protocol.
S5-U Interface: This interface is in between S-GW and P-GW. This interface will be used for data path. Under this interface UDP will be used for transport protocol and GTP-U will be used for application protocol.
S6a Interface: This interface is in between MME and HSS. This interface will be used for Authentication, Authorization and Accounting. The SCTP will be used for transport protocol and Diameter will be used for application protocol.
Functionality of LTE Nodes:
eNodeB
The following functionality for eNodeB in LTE network:
MME
The different functionality of MME are:
S6a Interface: This interface is in between MME and HSS. This interface will be used for Authentication, Authorization and Accounting. The SCTP will be used for transport protocol and Diameter will be used for application protocol.
Functionality of LTE Nodes:
eNodeB
The following functionality for eNodeB in LTE network:
- Header compression and user plane ciphering;
- MME selection when no routing to an MME can be determined from the information provided by the UE;
- UL bearer level rate enforcement based on UE-AMBR and MBR via means of uplink scheduling
(e.g. by limiting the amount of UL resources granted per UE over time);
(e.g. by limiting the amount of UL resources granted per UE over time);
- DL bearer level rate enforcement based on UE-AMBR;
- UL and DL bearer level admission control;
- Transport level packet marking in the uplink, e.g. setting the DiffServ Code Point, based on the QCI of the associated EPS bearer;
- ECN-based congestion control.
MME
The different functionality of MME are:
- NAS signalling;
- NAS signalling security;
- Inter CN node signalling for mobility between 3GPP access networks (terminating S3);
- UE Reachability in ECM-IDLE state (including control and execution of paging retransmission);
- Tracking Area list management;
- Mapping from UE location (e.g. TAI) to time zone, and signalling a UE time zone change associated with mobility,
- PDN GW and Serving GW selection;
- MME selection for handovers with MME change;
- SGSN selection for handovers to 2G or 3G 3GPP access networks;
- Roaming (S6a towards home HSS);
- Authentication;
- Authorization;
- Bearer management functions including dedicated bearer establishment;
- Lawful Interception of signalling traffic;
- Warning message transfer function (including selection of appropriate eNodeB);
- UE Reachability procedures.






No comments:
Post a Comment